Aquaculture carbon footprint
Increasing awareness of environmental impact and climate change has brought attention to the carbon footprint of various industries, including aquaculture.
Zeinab Abediostad
Aquaculture Specialist
22/06/2023

This blog post explores the concept of carbon footprint in aquaculture, highlighting its significance in understanding and mitigating the environmental impact of the industry.
What is the carbon footprint and how is it calculated?
The carbon footprint, a key indicator of the environmental effect and climate change contribution, calculates the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by human activities. It becomes crucial to precisely measure each operation's carbon footprint to get a detailed insight into the ecological effects of various processes, especially those within industries and enterprises. It is essential to guarantee an accurate assessment of the carbon footprint given the considerable contribution of GHG emissions to climate change and their profound repercussions for the environment and human well-being.
Determining GHG emissions in aquaculture requires adherence to established methodologies like the GHG Protocol and ISO 14064-1. These standardized approaches guarantee that data consistency, accuracy, and comparability are maintained throughout the calculation process. Carbon footprint calculators, both online (e,g., Climate Neutral Now and 2030 Calculator) and software-based (e.g., Carbon Footprinting Software by Carbon Trust, GHG Emissions Management Software solution by Enablon), are valuable tools that assist individuals and organizations in assessing their environmental impact. However, it is also recommended to take into account hiring experts with knowledge and experience in carbon management.
Aquaculture's carbon footprint is important to address due to its negative impact on the environment, human health, and ecosystems. Carbon footprint calculators consider factors like energy usage, travel patterns, dietary preferences, and product parameters to estimate it. Reducing emissions through measures like feed optimization and energy-saving techniques is crucial to mitigate harmful consequences. Improved waste management and sustainable aquaculture practices are also critical. Additionally, minimizing water contamination, preventing the introduction of alien species, and using sustainable aquaculture feed are necessary to reduce environmental impact (FAO, 2019).
Feed production, the use of energy and water, waste management, production processes, transportation, and the use of antibiotics and pesticides are some of the factors that can affect the carbon footprint of aquaculture. By optimizing such parameters, aquaculture's carbon footprint can be reduced. The primary sources of GHG emissions in aquaculture include fossil fuel consumption for farm operations, transportation-related emissions, and emissions from wild fish processed for feed production. Addressing energy efficiency, alternative energy sources and sustainable transportation methods can help minimize GHG emissions in the sector.
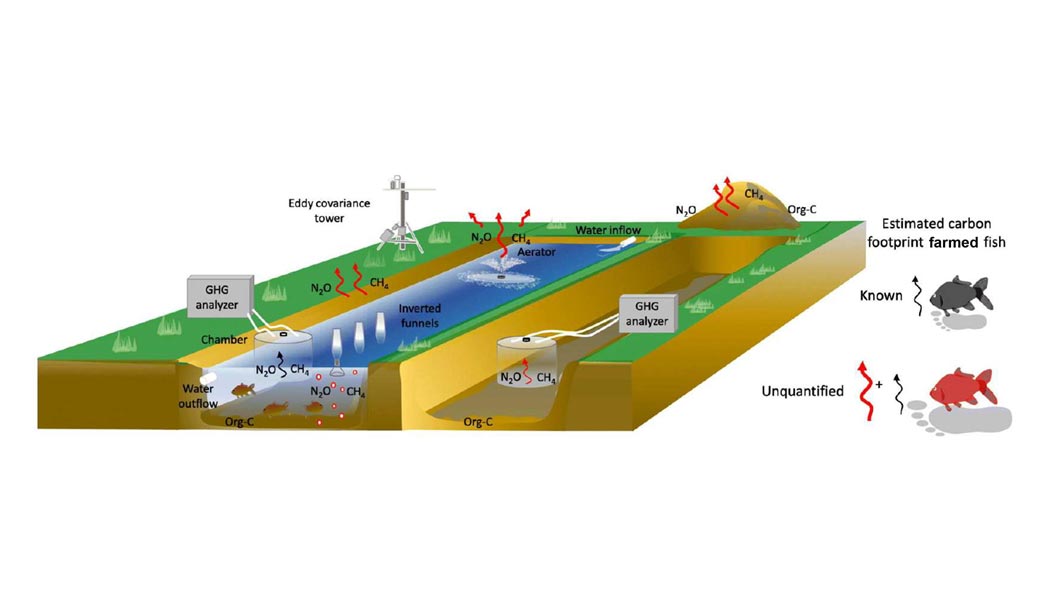
“Do we really know how much is the aquaculture carbon footprint?”
Measuring aquaculture carbon footprint
WWF notes that aquaculture has difficulty lowering its carbon footprint. These include the high cost of implementing sustainable practices, the difficulty in measuring emissions accurately, the lack of regulatory frameworks, the scarcity of sustainable technologies, and the low demand for seafood products made sustainably. A precise and widely accepted method for calculating the carbon footprint of aquaculture has yet to be discovered, despite extensive research and exploration of numerous sources.
The EU Aquaculture Advisory Council (AAC) advises the European Commission to consider the recommendation of conducting life cycle analyses for all aquaculture operations within the European Union. This includes carrying out assessments of the environmental impact of the products throughout their life cycle. Tools like AquaCal have been developed to simplify the process by incorporating relevant data sources.
Livestock production significantly impacts global GHG emissions because it accounts for 14.5% of all emissions. Aquaculture is thought to have a smaller carbon footprint than other agricultural practices, accounting for about 0.7% of global emissions (MacLeod et al. (2020)). Nevertheless, this can vary depending on production techniques, feed sources, and energy use. As an example, the World Bank estimates that cattle and fisheries now consume 1 billion tons of formulated feed, which indirectly adds 16 million tons of carbon to aquaculture systems. Increased emissions could result from the growing demand for protein from aquaculture.
According to MacLeod et al. (2020), aquaculture contributed around 0.49% of the world's anthropogenic GHG emissions in 2017, including those from fish caught for food. The sector is currently excluded from the Industrial Emissions Directive, which could notably help to manage its carbon impact. Its particular issues and concerns must be carefully considered before carbon footprint monitoring can be extensively used (CIWF, 2023).
Examples of sustainable aquaculture practices
Certificates used for farmed fish, like the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) or the Global Seafood Alliance (GSA), typically focus on environmental, social, and food safety assessments rather than including carbon footprint information in their certificates. However, certification requirements can change, so checking with the certifying company for the most recent data is advisable.
Sustainable aquaculture practices, e.g., using renewable energy sources, improving feed efficiency, adopting sustainable production methods, and enhancing transportation efficiency, contribute to minimizing the environmental impact of aquaculture. Some examples include Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) and sustainable feed sourcing.
In summary, in AWO, we consider it essential to effectively assess and comprehend aquaculture’s carbon footprint to identify opportunities for improvement, establish standards, and steer the adoption of sustainable methods. The aquaculture sector can contribute to a more environmentally friendly and sustainable future by implementing measures to reduce environmental impact and encouraging eco-conscious practices.
Related content




